Electric vs. Gas vs. Hybrid Cars: What’s the Difference?
As the automotive industry evolves, consumers have more choices than ever when it comes to vehicle powertrains. The traditional gas-powered car is no longer the only option—electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids are gaining popularity due to advancements in technology, environmental concerns, and rising fuel costs.
But what exactly is the difference between electric, gas, and hybrid cars? In this post, we’ll break down how each type of vehicle works, their pros and cons, and which one might be the best choice for your driving needs.
1. Gas-Powered Cars
How They Work
Gasoline cars use an internal combustion engine (ICE) to generate power. Fuel is mixed with air, compressed, and ignited by spark plugs inside the engine. This process creates energy, which powers the wheels.
Pros of Gas Cars
✔ Wide Availability – Gas stations are everywhere, making refueling convenient.
✔ Lower Initial Cost – Gas-powered vehicles generally cost less upfront compared to electric and hybrid cars.
✔ Longer Driving Range – Most gas cars can travel 300-400 miles on a full tank, and refueling takes just a few minutes.
✔ More Model Choices – There is a wider variety of gasoline-powered vehicles, from economy cars to high-performance sports cars.
Cons of Gas Cars
❌ Higher Fuel Costs – Gasoline prices fluctuate and can be expensive over time.
❌ Environmental Impact – Gas cars produce carbon emissions, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
❌ More Maintenance Required – Oil changes, spark plugs, and other engine-related maintenance are needed regularly.
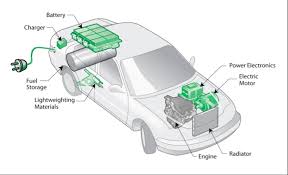
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
How They Work
Electric cars are powered by a battery and an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine. They must be charged via a home charger or a public charging station.
Pros of Electric Cars
✔ Zero Emissions – EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
✔ Lower Operating Costs – Electricity is usually cheaper than gasoline, and maintenance costs are lower since EVs have fewer moving parts.
✔ Smooth and Quiet Ride – Electric motors provide instant torque, leading to fast acceleration and a quiet driving experience.
✔ Government Incentives – Many governments offer tax credits and rebates for purchasing EVs.
Cons of Electric Cars
❌ Higher Initial Cost – EVs tend to have a higher purchase price due to battery costs.
❌ Charging Infrastructure – While charging stations are expanding, they are still not as widespread as gas stations.
❌ Longer “Refueling” Time – Charging can take anywhere from 30 minutes (fast charging) to several hours (home charging).
❌ Limited Range – Most EVs offer between 200-400 miles per charge, but range anxiety can be an issue for long-distance travel.
3. Hybrid Vehicles
How They Work
Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. There are two main types of hybrids:
- Standard Hybrid (HEV) – Uses both the gas engine and electric motor. The electric motor assists during acceleration, and the battery recharges while driving.
- Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV) – Can be charged via an electrical outlet and drive short distances (typically 20-50 miles) on electric power alone before switching to gasoline.
Pros of Hybrid Cars
✔ Better Fuel Economy – Uses less gasoline than a traditional gas car, saving money on fuel.
✔ No Range Anxiety – The gas engine provides backup when the electric battery runs out.
✔ Lower Emissions – Produces fewer emissions than traditional gasoline cars.
✔ Regenerative Braking – Uses braking energy to recharge the battery, improving efficiency.
Cons of Hybrid Cars
❌ More Expensive Than Gas Cars – Hybrids typically cost more than their gasoline-only counterparts.
❌ Higher Maintenance Costs – While hybrids have fewer moving parts than gas cars, the complexity of combining an engine and electric motor can lead to costly repairs.
❌ Limited Electric-Only Range (for HEVs) – Standard hybrids cannot drive solely on electricity for long distances.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Gas Car 🚗 | Electric Car ⚡ | Hybrid Car 🔋⛽ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Gasoline Engine | Battery & Electric Motor | Gasoline Engine + Electric Motor |
| Fueling Method | Gasoline Pump | Charging Station | Gasoline + Charging (PHEV) |
| Emissions | High | Zero | Lower than Gas Cars |
| Fuel Economy | Least Efficient | Most Efficient | More Efficient than Gas Cars |
| Driving Range | 300-400 miles | 200-400 miles | 400-600 miles |
| Refueling Time | 5 minutes | 30 min – 12 hours | 5 min (gas), 1-4 hours (PHEV charging) |
| Initial Cost | Lowest | Highest | Mid-Range |
| Maintenance Cost | High | Low | Moderate |
| Best For | Long trips, rural areas, performance cars | Environmentally conscious drivers, city driving | Balanced mix of gas efficiency and electric power |
Which One is Right for You?
Choosing between an electric car, gas car, or hybrid depends on your lifestyle, budget, and driving habits. Here’s a quick guide:
🚗 Choose a Gas Car if:
- You frequently take long road trips and don’t want to worry about charging.
- You’re looking for a lower upfront cost.
- You prefer traditional cars with widely available fuel sources.
⚡ Choose an Electric Car if:
- You want an environmentally friendly, emission-free vehicle.
- You mostly drive in urban or suburban areas with access to charging stations.
- You want lower operating and maintenance costs in the long run.
🔋⛽ Choose a Hybrid Car if:
- You want better fuel efficiency without worrying about charging infrastructure.
- You drive both short and long distances and want a flexible vehicle.
- You’re looking for a compromise between gas savings and convenience.
Final Thoughts
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, and consumers now have more powertrain options than ever. Gasoline cars offer reliability and convenience, electric vehicles provide sustainability and cost savings over time, and hybrids deliver a balance of both worlds.
As technology advances, charging infrastructure grows, and battery efficiency improves, electric and hybrid cars are becoming more practical choices for everyday drivers. However, gas-powered cars still remain the dominant choice for long-distance driving and high-performance vehicles.
No matter what you choose, understanding the differences between these vehicle types can help you make an informed decision based on your needs and budget.
Thinking about switching to an EV or hybrid? Research government incentives, available models, and charging options in your area before making the leap. Happy driving! 🚘⚡⛽